September 11, 2020
Acoustics + Performance
Acoustics - Performance Talking Points
Summary
Acoustics have a dramatic impact on performance of workers, students, and instructors through distraction, poor concentration, and speech inaudibility. Satisfaction is diminished since these issues can compound and lead to employee loss. Regarding open-office plans, productivity and satisfaction can be diminished, but research shows that employees prone to these characteristics will exhibit them regardless of the environment.
Keywords
Auditory distraction, performance, cognition, noise, open-plan office
Reduced Noise Levels
- Benefits to hospital staff:
- Improved acoustics contribute to decreased strain on staff, facilitating an increased capacity to care Improved acoustic conditions in the healthcare environment also reduce risks of conflicts and errors (Tiesler 2015)
- Reduced noise and distractions contribute to reducing errors in medication preparation (Tiesler 2015)
- Benefits to educational staff and students:
- “Very good” acoustic treatments give high absorption of noise with high “speech intelligibility”, so neither students nor instructors have to speak louder or repeatedly to their audience over short distances (Tiesler 2015).
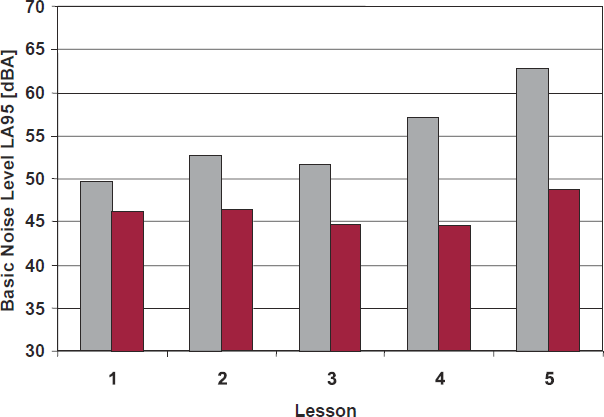
Base Noise Level observed in classrooms over all lessons conducted in the morning. Data reflects instructors reported Bad (grey) and Very Good (maroon) room acoustics (Tiesler 2015).
Increased Noise Levels
- Noise can decrease performance of tasks involving writing and math, particularly from speech (Kaarlela 2009).
- Poor acoustics can lead to environmental dissatisfaction and can affect workers’ performance (Kaarlela 2009).
- Coping strategies such as leaving one’s desk, switching workstations or working more slowly contributed to a direct loss of work performance.
- Office workers concentration is often impaired by offices sounds such as unanswered phones and background speech.
- Speech intelligibility is a common complaint from the combination of poor acoustics and noise.
- Intelligibility and volume of speech influence distraction, annoyance and productivity (Mak 2012).
Classroom Performance
- Reverberation time affects both students and teachers (Kristiansen 2013).
- Children whose classrooms had long reverberation performed worse and had worse relations to their peers and teachers than children from classrooms with short reverberation (Kristiansen 2013).
- Reverberation time as well as noise exposure had an effect on job satisfaction, lack of energy, and interest in leaving the job for school teachers (Kristiansen 2013).
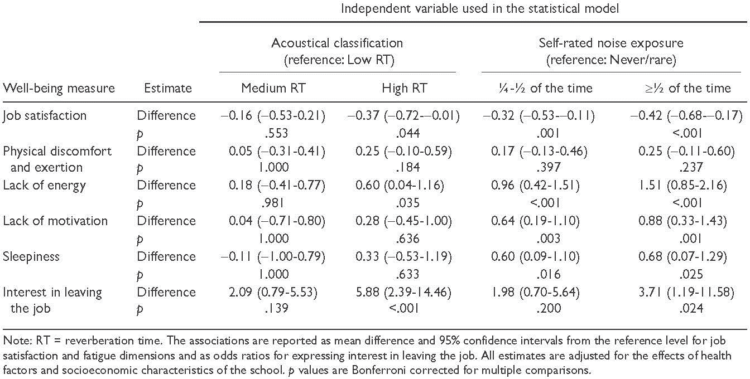
Effects of acoustic classification and noise exposure on Well-Being Indicators (Kristiansen 2013).
Open-Plan Offices
- Drawbacks:
- Open-plan offices have higher rates of noise disturbance than private offices (Kaarela 2009).
- Exposure to office noise negatively impacted ratings of adverse perceptions, selected symptoms, and self-assessed performance, but not necessarily the performance of office tasks (Kaarela 2009).
- Caveats:
- Occupants who are typically disturbed by open-plan office noise responded differently to noise than those who are not (Kaarela 2009).
- Noisiness of open-plan offices is not an intrinsic quality, time-averaged SPLs (Sound Pressure Levels) over the working day were practically the same as typical offices filled with cubicle (Kaarela 2009).
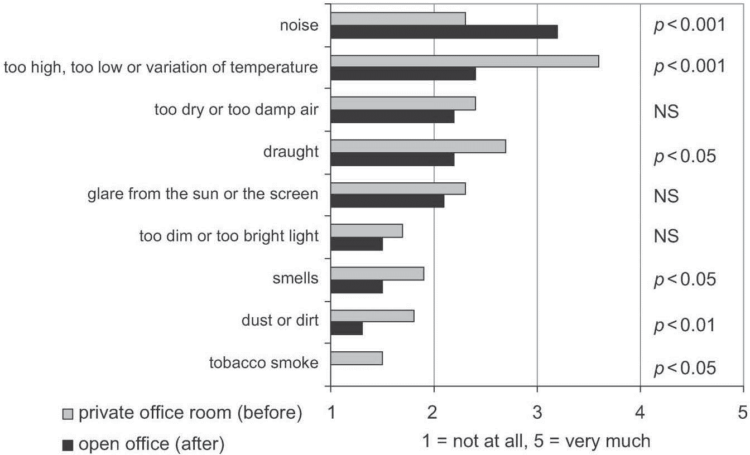
How much have the following indoor environmental factors disturbed you at your workstation during the last 3 months? Mean values and the significance of change (p-value) (Kaarela 2009).
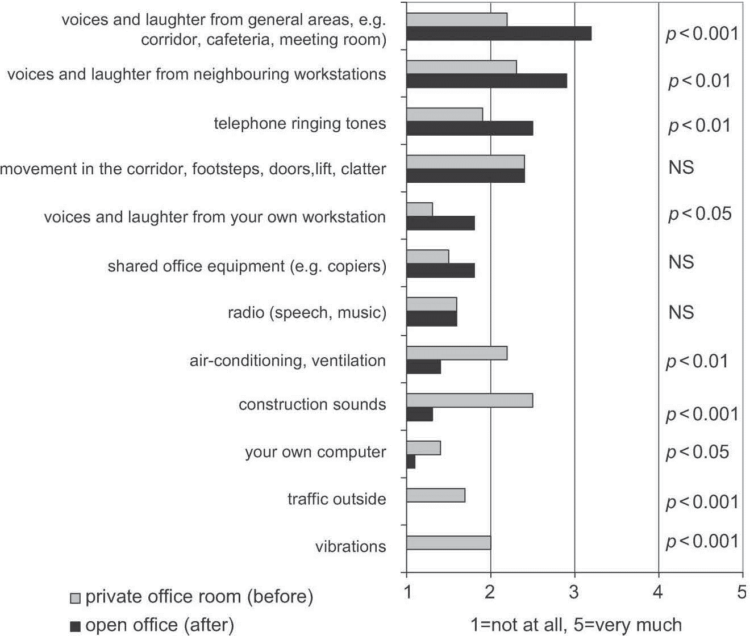
How much do the following sounds disturb your concentration on your work at your workstation? Mean values and the significance of change (p-values) (Kaarela 2009).
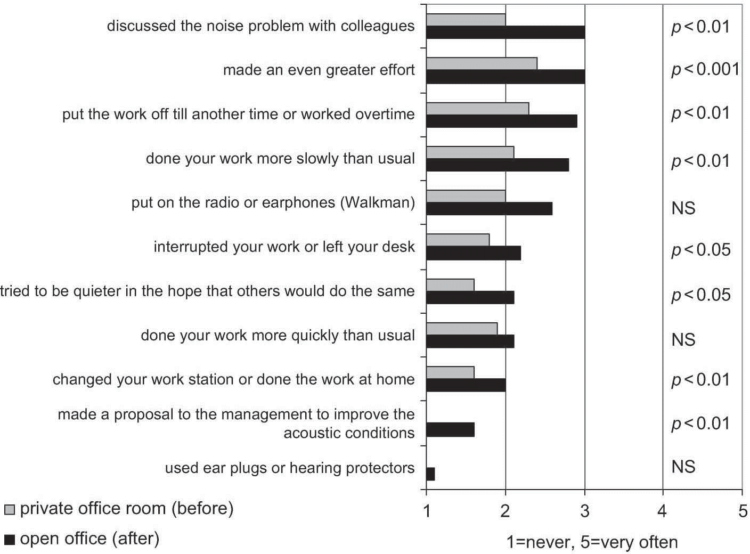
How often do you act in the following way to cope with your work because of the sounds in your work environment? Mean values and the significance of change (p-value) (Kaarela 2009).
Key References
